What is Light Pollution?
“Losing the Dark” an IDA Film
What is Light Pollution?
Most of us are familiar with air, water, and land pollution, but did you know that light can also be a pollutant?
The inappropriate or excessive use of artificial light – known as light pollution – can have serious environmental consequences for humans, wildlife, and our climate. Components of light pollution include:
- Skyglow – brightening of the night sky over inhabited areas
- Glare – excessive brightness that causes visual discomfort
- Light trespass – light falling where it is not intended or needed
- Clutter – bright, confusing and excessive groupings of light sources
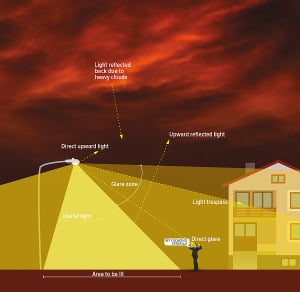
The infographic above illustrates the different components of light pollution and what “good” lighting looks like. (Image by Anezka Gocova, in “The Night Issue”, Alternatives Journal 39:5 (2013). Click to enlarge.
Light pollution is a side effect of industrial civilization. Its sources include building exterior and interior lighting, advertising, commercial properties, offices, factories, streetlights, and illuminated sporting venues.
The fact is that much outdoor lighting used at night is inefficient, overly bright, poorly targeted, improperly shielded, and, in many cases, completely unnecessary. This light, and the electricity used to create it, is being wasted by spilling it into the sky, rather than focusing it on to the actual objects and areas that people want illuminated.
Light Pollution Effects on Wildlife and Ecosystems
For billions of years, all life has relied on Earth’s predictable rhythm of day and night. It’s encoded in the DNA of all plants and animals. Humans have radically disrupted this cycle by lighting up the night.
Plants and animals depend on Earth’s daily cycle of light and dark rhythm to govern life-sustaining behaviors such as reproduction, nourishment, sleep and protection from predators.
Scientific evidence suggests that artificial light at night has negative and deadly effects on many creatures including amphibians, birds, mammals, insects and plants.
Artificial Lights Disrupt the World’s Ecosystems
Nocturnal animals sleep during the day and are active at night. Light pollution radically alters their nighttime environment by turning night into day.
According to research scientist Christopher Kyba, for nocturnal animals, “the introduction of artificial light probably represents the most drastic change human beings have made to their environment.”
“Predators use light to hunt, and prey species use darkness as cover,” Kyba explains “Near cities, cloudy skies are now hundreds, or even thousands of times brighter than they were 200 years ago. We are only beginning to learn what a drastic effect this has had on nocturnal ecology.”
Glare from artificial lights can also impact wetland habitats that are home to amphibians such as frogs and toads, whose nighttime croaking is part of the breeding ritual. Artificial lights disrupt this nocturnal activity, interfering with reproduction and reducing populations.
Artificial Lights Can Lead Baby Sea turtles to their Demise
Sea turtles live in the ocean but hatch at night on the beach. Hatchlings find the sea by detecting the bright horizon over the ocean. Artificial lights draw them away from the ocean. In Florida alone, millions of hatchlings die this way every year.
Artificial Lights have Devastating Effects on Many Bird Species

Birds that migrate or hunt at night navigate by moonlight and starlight. Artificial light can cause them to wander off course and toward the dangerous nighttime landscapes of cities. Every year millions of birds die colliding with needlessly illuminated buildings and towers. Migratory birds depend on cues from properly timed seasonal schedules. Artificial lights can cause them to migrate too early or too late and miss ideal climate conditions for nesting, foraging and other behaviors.
Ecosystems: Everything is Connected
Many insects are drawn to light, but artificial lights can create a fatal attraction. Declining insect populations negatively impact all species that rely on insects for food or pollination. Some predators exploit this attraction to their advantage, affecting food webs in unanticipated ways.
